adverse impact analysis statistical tests|adverse impact vs disparate treatment : bespoke adverse impact are statistical significance tests and practical significance tests. Statistical Significance Tests A . z-test of independent proportions, often called the „2 standard deviation‟ test, is a statistical technique that translates the probability of . a difference. in selection rates into the metric of standard deviations.
03/02/2022 12h12. A caminhoneira e youtuber Aline Füchter Ouriques, conhecida por seu canal com mais de 1,5 milhão de seguidores, comemora cada pequena vitória após o acidente que quase tirou sua vida, no dia .
{plog:ftitle_list}
en el día de Disney+ se revelan las primeras imágenes de la .
Statistical Methods for Adverse Impact Analyses. Two statistical significance tests are most commonly used to analyze data for the purpose of identifying AI. They are: the 2 standard deviation (SD) test, also called the Z test, and Fisher’s exact test (FET).Statistical tests evaluate the relationship between two or more variables that are measured in a sample. In the context of adverse impact, statistical tests assess the relationship between group membership (e.g., a particular race or sex) and decision outcome (e.g., pass/fail, hired, .Affirmative Action. We first define adverse impact and review legislative history and important case law. Next, we present a brief overview of the different adverse impact statistics that employers can consider for analysis of their Affirmative Action Plan data, and recommend a .
custom moisture meter trees
The 2 most common methods for assessing adverse impact, the four-fifths rule and the z-test for independent proportions, often produce discrepant results. These discrepancies are due to the focus on practical vs statistical significance, and on differing operational definitions of adverse .Statistical significance has long played an important role in the evaluation of employment disparities. Significance tests are frequently referenced by the courts when evaluating disparate impact discrimination claims (Esson & Hauenstein, 2006), as well as in audits of employment .
adverse impact are statistical significance tests and practical significance tests. Statistical Significance Tests A . z-test of independent proportions, often called the „2 standard deviation‟ test, is a statistical technique that translates the probability of . a difference. in selection rates into the metric of standard deviations. Yep. Yep, great question. So look, remember, if you have an indicator of adverse impact analysis, it does not mean that discrimination has taken place. Adverse impact indicators can be rebutted with the right .Statistical Methods for Adverse Impact Analyses Two statistical significance tests are most commonly used to analyze data for the purpose of identifying AI. They are: the 2 standard deviation (SD) test, also called the Z test, and Fisher’s exact test (FET). Both approaches examine the relationship between two variables to
But the absence of adverse impact of the test in the aggregate does not end the inquiry. For there may be discrimination or adverse impact in the assignment of individuals to, or in the selection of persons for, particular jobs. . methods of job analysis or statistical techniques? A: No. The Guidelines are concerned with the validity and .Statistical tests of adverse impact test the following hypothesis (or null hypothesis): There is no relationship between group membership and decision outcome (i.e., subgroups do not differ in decision outcome; there is no adverse impact); any observed difference is due to chance.
Testing for adverse impact when sample size is small. Journal of Applied Psychology, 93, 463-471. Dunleavy, E. M., & Gutman, A. (2011). An update on the statistical versus practical significance debate: A review of Stagi v Amtrak (2010). The Industrial-Organizational Psychologist. 48, . Adverse Impact Analysis: Understanding Data, Statistics . Adverse impact results from company hiring practices that negatively affect protected classes. It is typically determined on the basis of the 4/5ths Rule (which is violated when the minority selection rate is less than 4/5ths of the majority selection rate) or a chi-square test of statistical independence (which is violated when group membership is associated with hiring .The statistical field has convened at a consensus that the FET can only be accurately applied in the first model—the Independence Trial Model. Because this model does not represent typical personnel selection data, “there is reason to question the appropriateness of the FET for adverse impact analysis” (Collins & Morris, 2008). Statistical significance is a function of multiple factors, including the magnitude of the disparity, the number of observations in the analysis, and the power of the statistical test used. The purpose of a statistical test is to assess the likelihood that random or legitimate, nondiscriminatory factors rather than discriminatory factors .
The statistical test results are also automatically computed and shown in the bottom right portion of Adverse Impact Analysis.The results show that that the p-value associated with this sample is 0.29, which is not less than the 0.05 alpha level; therefore, the . Employers now have a wide variety of algorithmic decision-making tools available to assist them in making employment decisions, including recruitment, hiring, retention, promotion, transfer, performance monitoring, demotion, dismissal, and referral. Employers increasingly utilize these tools in an attempt to save time and effort, increase objectivity, optimize employee .
Practical Tests. When sample sizes are small, a change of only a few individuals could result in different adverse impact outcomes. Practical tests help guide decisions regarding the existence of adverse impact when samples are small.
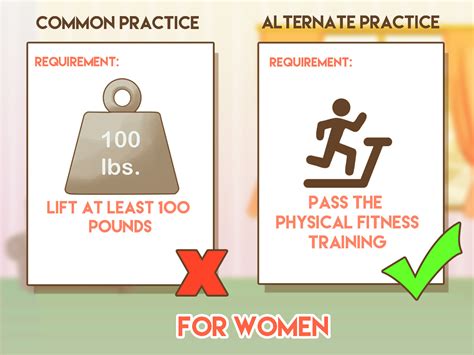
This method of analysis is consistent with the seminal Supreme Court . whether a test or other selection procedure has a disparate impact on a particular group ordinarily requires a statistical analysis. If the selection procedure has a disparate . The test had a significant adverse impact on women – prior to the use of the test, 46% of .adverse impact are statistical significance tests and practical significance tests. Statistical Significance Tests A . z-test of independent proportions, often called the „2 standard deviation‟ test, is a statistical technique that translates the probability of . a difference. in selection rates into the metric of standard deviations.Adverse Impact and the "four-fifths rule." - A selection rate for any race, sex, or ethnic group which is less than four-fifths (4/5ths) (or eighty percent) of the rate for the group with the highest rate will generally be regarded by the Federal enforcement agencies as evidence of adverse impact. Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures
Adverse Impact and Test Validation: A Practitioner's Handbook by Dan Biddle, PhD (ISBN: . Investigating Test Bias (using statistical models) . This book also includes evaluation copies of BCG's new Test Validation & Analysis .Sample size required for adverse impact analysis. Applied HRM Research, 6(1-2), 13-32. Morris, S. B., & Lobsenz, R. E. (2000). Significance tests and confidence intervals for the adverse impact ratio. Personnel Psychology, 53(1), 89-111. . and thus there is no evidence of disparate impact based on this statistical test. This corroborates what . In order to provide a more consistent framework for evaluating adverse impact, a new significance test is proposed, which is based on the same effect size as the four-fifths rule. Although this new test was found to have slightly better statistical power under some conditions, both tests have low power under the typical conditions where adverse .
The purpose of these frequently asked question is to provide clarifying and educational information about what constitutes a selection procedure that is subject to the Uniform Guidelines on Employee Selection Procedures (UGESP) at 41 CFR Part 60-3, how OFCCP identifies selection disparities, and how OFCCP investigates and reviews matters related to .Calculating Adverse Impact. Adverse Impact Analysis is a quick and easy to use tool that can estimate adverse impact using a variety of both statistical and practical tests. It includes tests that have been historically recommended by Federal regulators as well as cutting edge tests arising out of the latest research.• statistical significance test, • adverse impact results, and • Judge‟s ruling. See Table 1 on page 8 for a detailed list of all included cases. Of the 29 cases, eleven included only a practical significance measure to detect adverse impact (e.g., 4/5th rule, „naked eye‟ comparison of the difference in subgroup selection rates,
A "substantially different" rate is typically defined in government enforcement or Title VII litigation settings using the 80% Rule, statistical significance tests, and/or practical significance tests. Adverse impact is often used interchangeably with "disparate impact", which was a legal term coined in one of the most significant U.S. Supreme .
Pooled Two-Sample Z-Score Test. The pooled two-sample z-score test is the statistical test recommended by the Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (see p. 383). It is also referred to as the Z-test of the difference in selection rates (or Z D) or the two standard deviation test (or 2-SD).The Z D test is a statistical test that assesses the difference between two .Statistical Analysis of Adverse Impact. Barrett, R. S. (1998). Challenging the Myths of Fair Employment Practices. . Westport, CT: Quorum. Biddle, D. (2005). Adverse Impact and Test Validation: A Practitioner’s Guide to Valid and Defensible Employment Testing. . Sample size required for adverse impact analysis. Applied HRM Research, 6, 13 .
Adverse Impact Analysis / Four-Fifths Rule. In 1978, four government agencies (EEOC, Department Of Labor, Department of Justice, and the Civil Service Commission) adopted a set of guidelines known as the Uniform Guidelines for Employee Selection Procedures, which provided information on what constitutes a discriminatory test surrounding employment testing, as well . Background Statistical methods for the analysis of harm outcomes in randomised controlled trials (RCTs) are rarely used, and there is a reliance on simple approaches to display information such as in frequency tables. We aimed to identify whether any statistical methods had been specifically developed to analyse prespecified secondary harm outcomes . Although possible, incorporating chi-square, Fisher's exact, or Lancaster's mid-P test estimates is more complex, in that for these tests, the criteria for statistical significance vary by sample .
how to calculate adverse impact
Resultado da 720p. novinha gostosa fazendo sexo boquete caiu na net ninfeta safada. 72 sec Portoo1 -. Videos de sexo com novinha gostosa fodendo caiu na net .
adverse impact analysis statistical tests|adverse impact vs disparate treatment